Learn all about Working Principles, Cathodes, Anodes and Electrolytes
What you will learn
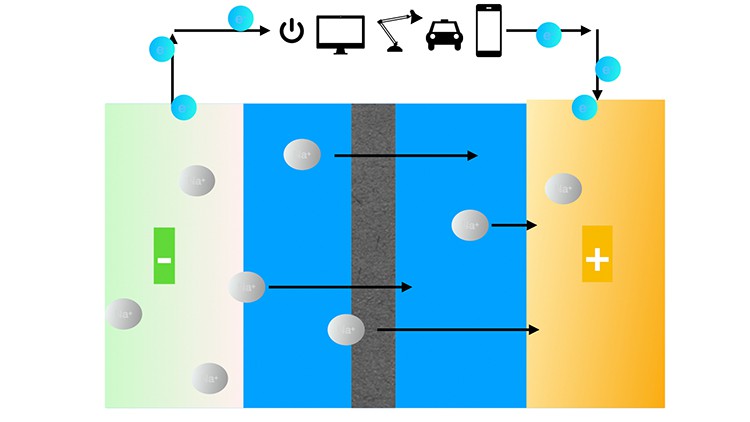
Working Principle of a Na-ion Batteries, Advantages and Problems
Overview on Cathode Materials
Overview on Anode Materials
Overview on Electrolytes
Description
Do you have read in newspapers that several companies want to release this so called “sodium-ion battery”?
Are you curious to learn more about this technology?
Or maybe you are a Scientist and need quickly get started in this topic?
Then this class is for you.
We will cover all general things about the sodium-ion battery also called “SIB” such as Working Principle, Advantages, Problems, Current Market.
And also do a deeper dive in the different materials. Such as the cathode systems (Oxide, Prussian blue, Polyanionic compounds) as well as in Anode (carbons, alloys…) and finally have a look to promising electrolytes (liquid, polymer and solid).
We will cover one by one the different compounds, with examples on their performance, the advantages and which problems still remains.
With this you will have all basic in the hand in order to continue on your own to study more deeply this brand-new battery system.
!!!! Please: have a look to the content and also watch the free lessons in order to assess is the class is for you!!!!
before buying it
Beware: this class is not meant for absolute beginner. We will dive directly into the materials and principle and I will not give an introduction in chemistry. So it is best to buy this class, if you have a good background in chemistry, material science or energy science.
This class is only theoretical, and does not cover any experimental demonstrations or similar.
If you have doubt, please watch the different free lessons, or send me a question. And do not hesitate to use your 30-day money back guarantee in case you realize that the class is not what you look for.
For this class I mainly use the book sodium-ion battery from Xie, Wu and Huan. And I will cite and add a lot of publications and reviews, so that you can go on yourself for reading
Content