A step by step the Matlab codes for BER estimations of different Comm. systems like OFDM and NOMA Comm. systems
⏱️ Length: 3.5 total hours
⭐ 4.32/5 rating
👥 14,765 students
🔄 February 2021 update
Add-On Information:
Note➛ Make sure your 𝐔𝐝𝐞𝐦𝐲 cart has only this course you're going to enroll it now, Remove all other courses from the 𝐔𝐝𝐞𝐦𝐲 cart before Enrolling!
- Course Overview
- Comprehensive exploration of the Physical Layer (PHY) dynamics in modern wireless communication, focusing on the transition from mathematical theory to functional Matlab scripts.
- In-depth investigation into the architecture of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), detailing the process of subcarrier modulation, IFFT/FFT operations, and the critical role of cyclic prefixes in eliminating Inter-Symbol Interference.
- Advanced study of Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA), a cornerstone of 5G technology, focusing on power-domain multiplexing and the algorithmic implementation of Successive Interference Cancellation (SIC).
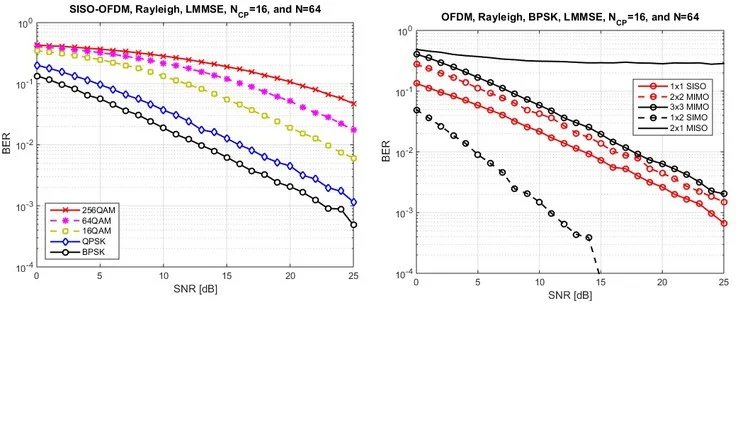
- Detailed analysis of Bit Error Rate (BER) performance across various channel conditions, providing a quantitative framework to evaluate the reliability of digital communication links.
- Structured walkthrough of signal degradation factors, including Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) and multipath fading environments, ensuring a realistic simulation of mobile radio propagation.
- Comparative performance evaluation of different M-ary modulation schemes, such as QPSK, 16-QAM, and 64-QAM, under diverse signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) scenarios.
- Insightful breakdown of pilot-based Channel Estimation techniques, allowing learners to understand how receivers compensate for dynamic channel fluctuations in real-time.
- Requirements / Prerequisites
- A fundamental understanding of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) concepts, including sampling theorems, discrete-time systems, and frequency-domain analysis.
- Basic literacy in Matlab programming syntax, specifically regarding matrix manipulations, loop structures, and conditional logic.
- Introductory knowledge of Communication Theory, such as the concepts of modulation, demodulation, and the basic structure of a transceiver system.
- A working installation of Matlab (2018b or newer recommended) with the Communications Toolbox installed to access specialized functions for waveform generation.
- Familiarity with Linear Algebra and probability theory to comprehend the statistical nature of noise and the mathematical modeling of fading channels.
- Skills Covered / Tools Used
- Monte Carlo Simulation: Mastering the iterative process of generating random data bits to estimate error probabilities with high statistical confidence.
- Matrix Vectorization: Utilizing Matlab’s native strengths to write optimized, high-speed code that avoids nested loops when processing large communication datasets.
- Visual Data Representation: Crafting professional-grade SNR vs. BER plots using logarithmic scales to visualize system performance trends effectively.
- Signal Constellation Mapping: Designing and implementing custom mappers and de-mappers to visualize how noise impacts signal points in the complex plane.
- Channel Modeling Tools: Leveraging Matlab functions to create Rayleigh and Rician fading objects, simulating the stochastic nature of urban and rural wireless environments.
- Error Control Coding: Implementing basic check-and-balance scripts to verify the integrity of received data packets against original transmissions.
- Benefits / Outcomes
- Bridge the Theory-Practice Gap: Develop the ability to translate complex equations found in engineering textbooks into executable and verifiable simulation models.
- Research Readiness: Gain the foundational skills required to conduct academic research or industrial R&D in the fields of B5G and 6G wireless standards.
- Portfolio Development: Build a repository of reusable Matlab scripts and functions that can be showcased to potential employers in the telecommunications sector.
- System Optimization Proficiency: Learn how to fine-tune system parameters, such as power allocation in NOMA or subcarrier spacing in OFDM, to maximize spectral efficiency.
- Enhanced Troubleshooting Skills: Develop a systematic approach to debugging communication algorithms by isolating noise effects from algorithmic errors.
- Competitive Edge in Telecommunications: Acquire specialized knowledge in high-demand areas like NOMA and OFDM, making you a more versatile candidate for wireless engineering roles.
- PROS
- Niche Focus: Unlike generic Matlab courses, this specifically targets high-level wireless protocols like NOMA, which is often underrepresented in standard curricula.
- Practical Coding Emphasis: The course prioritizes “learning by doing,” ensuring that every theoretical concept is immediately followed by a step-by-step coding demonstration.
- High Efficiency: With a total duration of 3.5 hours, the course provides a high information-to-time ratio, perfect for busy professionals and students.
- Proven Track Record: Boasting a strong 4.32/5 rating and over 14,000 students, the content has been vetted and refined based on extensive learner feedback.
- CONS
- Complexity Ceiling: The fast-paced nature of the advanced sections may require students to pause and perform additional self-study if they lack a strong background in stochastic processes.
Learning Tracks: English,Teaching & Academics,Engineering
Found It Free? Share It Fast!