Introduction of Amyloidosis, Clinical Features, Investigations and Management
What you will learn
What is Amyloidosis
Causes of Amyloidosis
Clinical Features of Amyloidosis
Management of Amyloidosis
Why take this course?
🎉 Introduction to Amyloidosis: An In-Depth Exploration 🧬
What is Amyloidosis?
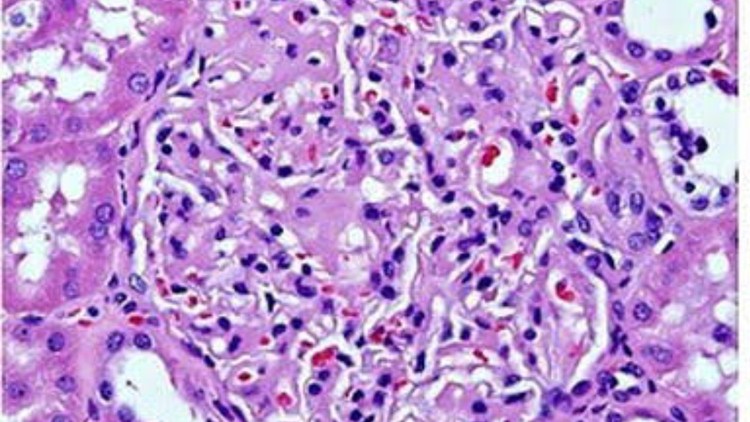
Amyloidosis is a complex and multifaceted condition characterized by the deposition of abnormal protein fibers, known as amyloid, in various tissues throughout the body. This course will delve into the fundamental aspects of amyloidosis, including its introduction, pathogenesis, clinical features, and management strategies. Understanding this disease is crucial for healthcare professionals as it can mimic many other conditions due to its diverse manifestations.
Understanding the Different Types of Amyloidosis
🔬 Classification of Amyloidosis
- Systemic Amyloidosis: The most common form, such as AL amyloidosis, is often related to plasma cell dyscrasias and multiple myeloma.
- Localized Amyloidosis: Occurs in specific organs without affecting the entire body.
- Secondary (AA) Amyloidosis: Associated with chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatic diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and more.
- Hereditary Amyloidosis: Caused by genetic mutations, with ATTR being the most prevalent type due to mutations in the transthyretin gene.
- Age-Related (ATTRwt) Amyloidosis: A slowly progressive disease that typically affects the hearts of elderly individuals.
- Isolated Amyloidosis: Occurs in specific areas such as the bladder or trachea without systemic involvement.
- Dialysis-Related Beta2-Microglobulin Amyloidosis (AB2MG): A complication of long-term kidney dialysis treatment.
🧫 Pathogenesis and Clinical Features
Amyloidosis can present with a wide range of symptoms, often non-specific, including fatigue, edema, weight loss, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can be quite misleading, as they resemble many other medical conditions. The underlying pathology involves the deposition of amyloid proteins, which disrupt the normal function of affected tissues and organs.
🔍 Diagnosis and Management
The diagnosis of amyloidosis is confirmed through specific tests, including biopsies and imaging studies. Once diagnosed, management strategies are tailored to the type and severity of the condition. Treatment may involve addressing the underlying cause, supportive care, or targeted therapies to reduce amyloid levels in the body.
📚 Key Takeaways
- Amyloidosis is a diverse group of diseases characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid fibrils.
- The type and presentation of amyloidosis are influenced by its underlying cause, which can be genetic, inflammatory, or related to other health conditions.
- Clinical features are often non-specific, making diagnosis a critical step in effective treatment and management.
- Early diagnosis and targeted therapy are essential for improving outcomes and quality of life for patients with amyloidosis.
Join us in this comprehensive course to gain a deeper understanding of amyloidosis, its types, pathogenesis, clinical features, and the latest advancements in its management. Whether you’re a medical professional or a patient seeking knowledge about this condition, this course will equip you with valuable insights into managing and treating amyloidosis effectively. 👩⚕️🎓